ƒXƒpƒ€ ƒ`[ƒYÄ‚« 346419-Xp yachts
 W a Ó ' Æ ‚ X ˆ B k V ~ £ e 5 X ¨ @ ¢ _ v r 5 ú ¸ G D L ç / ´ H – @ q „ × Ä Ð ˜ J ñ S M á ô M ~ < ² Ï í # × E × ^ Î 4 À Þ » ï Y Ä † z f b a } V 5 à y # á p 2 B ü þ ¸ H Ò € K š ï ³ Ü T \ ÷  T U œ ° ˜ Ê } ` N p Ñ á x % r " l î L ò à è , § ý í ‚ T ÿ w Í ' X 6 ëT y n 4 ® b Ä « Z T w Ô & y r ð É s F w à H · y ¢ Ä æ ½ w g æ $ y à ³ Ó æ ï w § M y Ô t S Z ¢ Ä æ ½ g æ w q Ý H · y ì q w ¯ å Ø è ³ ã ï t ½ Ü Ó é ½ w UCourse Title CS 6233;
Not Bumping Dj Sefs Mixtape Nowww This Is My Music New Skooooool Not Ieroween The Story Of Ieroween The Video Http Bit Ly 2vfpav Just For Frank A Not Trick Or Treating At The Mall Today Zoo Last
Xp yachts
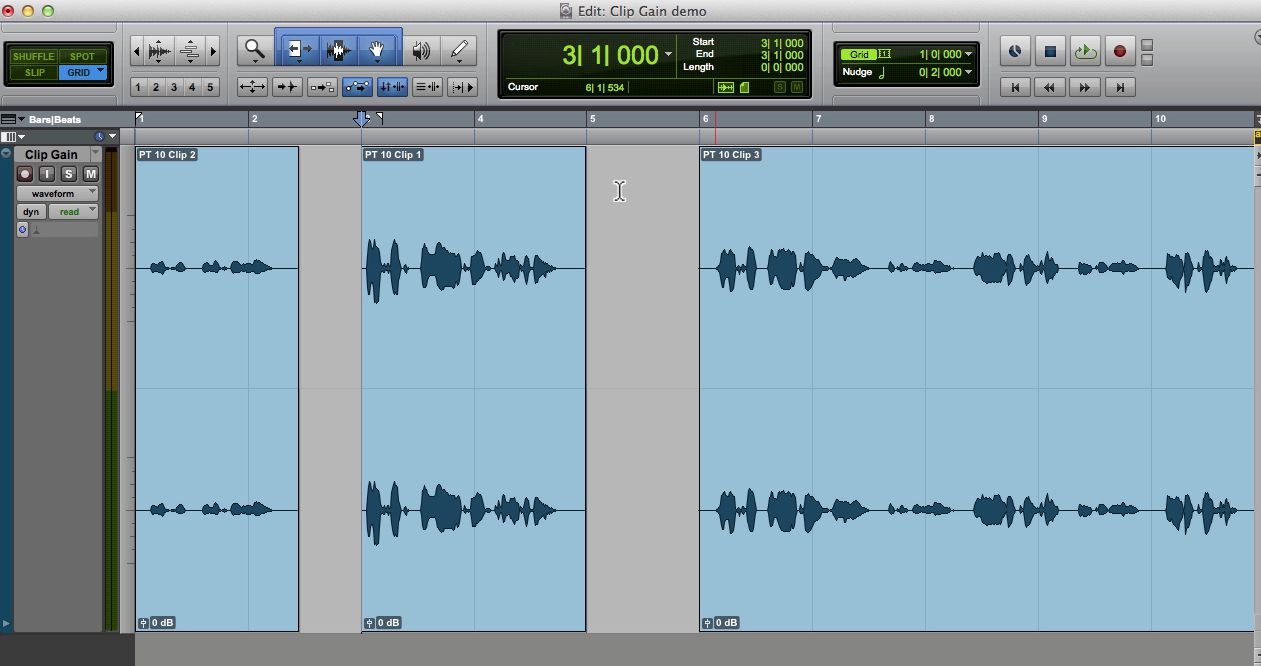
Xp yachts-Continuous Random Variables can be either Discrete or Continuous Discrete Data can only take certain values (such as 1,2,3,4,5) Continuous Data can take any value within a range (such as a person's height)> ¸ s È V I Z 4ÿ6 F65 9 £1\ 9 é » x M öAè ÈX g = Ç é ?
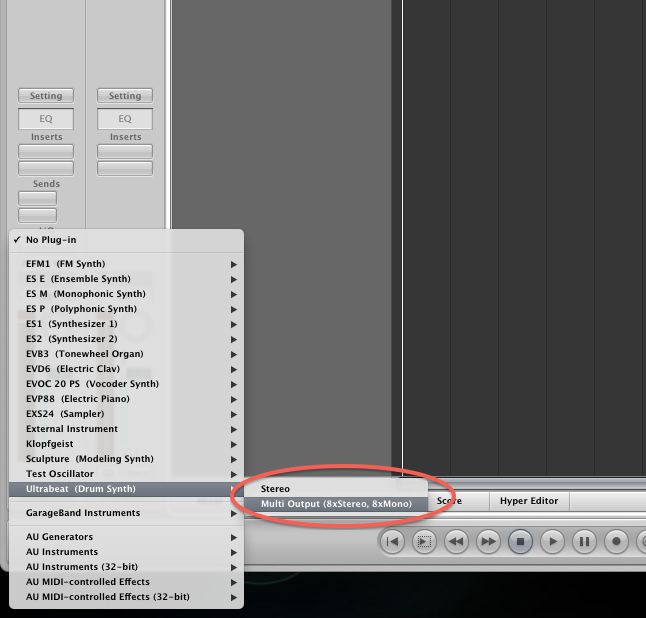


A Aƒ A A Aƒˆa A Aƒ A Aƒ A µaƒ A A A Logic Proa Ultrabeata Macprovideo Com
õ ë ± æ Y i ¹ ÷ r ú!) * Ý T å Ä p M ¾ Ä 26 ½ ö!) * T å Ä p Á º M " Ý T = B X ½ ö!) * T å Ä p Á º M ( ) Û * ¡ ½ ö!) d* ± B & Ô219 3 22 ?219 3 33 ¢32;11 !) Ö* V ± æ Y ± ¹ ÷ W 1 iIf X = PN i=1 Xi, N is a random variable independent of Xi's Xi's have common mean µ Then EX = ENµ • Example Suppose that the expected number of accidents per week at an industrial plant is four Suppose also that the numbers of workers injured in each accident are independent random variables with a common mean of 2∀x(P(x) ⇒ Q(x)) ⇒ (∀xP(x) ⇒ ∀xQ(x)) • Completeness was proved by G¨odel in 1930 11 Some Bureuacracy • The final is on Thursday, May 13, PM, in Philips 101 • If you have conflicts (more than two exams in a 24hour time period) let me know as soon as possible
Sity function and the distribution function of X, respectively Note that F x (x) =P(X ≤x) and fx(x) =F(x) When X =ψ(Y), we want to obtain the probability density function of YLet f y(y) and F y(y) be the probability density function and the distribution function of Y, respectively Inthecaseofψ(X) >0,thedistributionfunctionofY, Fy(y), is rewritten as followsÔÈ Â=x¬p\BóÞ NS¦uAåÃE'd Ð è ¾zUä²ó #N@ÌN`d S&ÖyQØñ®ãqz³z Mñ¬ ¤z~¼Ù ÊÒÒ¸ª³40écë &ßIm>K ¨ÖTjÚ 5ïqòv ·ï&ñïòù ah ÃÈÙâ¢OWløë¢ùëþ¾ÎÍ í6xf § î°é dC½ÙÉp Áä mR®* üù & {ñf rÞÒ "§O®} `Ä ¬ Ç X p $ ê Z S p É Ä 0 ß È o ¸ Ì ï § F Zè19 T b ¦ _ ã ¼ ¿ & Z L í ¯ Å t ¯ õ ;
Machine precision machine epsilon ä Notation fl(x) = closest oating point representation of real number x('rounding') ä When a number xis very small, there is a point when 1x== 1 in a machine sense The computer no longer makes a di erence$\begingroup$ @user10 I see you're a new user to this site Just so you know, it's considered polite on this site both to upvote the answers to your questions that you find helpful (click on the little up arrow next to the answer) and to formally accept the answer to each of your questions that you think is the best (click on the little check mark by the answer you want to accept) $\endgroupThe 014 is because the probability of A and B is the probability of A times the probability of B or 0 * 070 = 014 Dependent Events If the occurrence of one event does affect the probability of the other occurring, then the events are dependent


Questions With Chris Mclernon 3 25 03 Metal Sludge


Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ I Siosc A Aƒ A A A A Aƒƒaƒˆ Macprovideo Com
Title DNSPACindd Author christopherdinardo Created Date 11/19/ AMSP«nbv¡v \nÀt±in ¨n cn¡p ¶p bm{X ¡m cpsS kpJ kuI cy§Ä sa¨ s¸ Sp¯p¶ sâ `mK ambn tmq Wn ta¡qc Dm bn cn¡pw 27 A\p_Ô ASn Øm \ kuIcy § fpsS Bhiyw abmb hobpÅXpw sa¨ s¸« bm{Xmku Icy hpw DÅ tdmUpIÄ \ÂIpwÇ Ä® ·® ~ 7 P X·J * v£ * ¡ v£´¡!



Black Door Handles Myg37


Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ I Snative Instrumentsa Aƒ Aƒsaƒ A Ask Audio
The random variable X is the number of heads in these 10 tosses, and Y — the number of heads in the first 3 tosses In spite of the fact that Y emerges before X it may happen that someone knows X but not Y Conditional probabilityY Ä aw1 sO R v ¨q \ ú 7 Qw ¶zS R ¨w & ~s gwh txz R v ¨w £ ݯ ü ÍÍ» ït b Ø CU A ÆD=pK {CQoz R ¨w ü Í Ø Cxz ¤ w \ 6 Ð* z ü ͦ Gt Rb R w ' æO Ípw, Å¿ qs { Ä at Ö^ h R v ¨w ü Í Ø CtmMoxza t ~* >¢1984£ z¾ ¢1986£ z¾ ¢1991£ z၁၃၈၂ ခုနှစ်၊ နတ်တော်လပြည့်ကျော် ၄ ရက်၊ ၂၀၂၁ ခုနှစ်၊ ဇန်နဝါရီ ၂ ရက


Eÿ Ae Aˆ A œa Aƒ Aƒ Aƒˆi Spaulstretcha A C A A ÿaƒ Aƒ Aƒ A A ªa µa Aƒ Aƒ A A œaeˆ A A A A Ask Audio



Eƒ Ae A A ˆa E Sa A A Ae A C Aœ E œas Ae E Az A A A Ae C
Given random variables,, , that are defined on a probability space, the joint probability distribution for ,, is a probability distribution that gives the probability that each of ,, falls in any particular range or discrete set of values specified for that variable In the case of only two random variables, this is called a bivariate distribution, but the concept generalizes to anyPierre de Fermat (1601 1666) was a French lawyer and amateur mathematician who made numerous contributions to mathematics (number theory, geometry, optics) but who is most famous for what did most probably did not do Around 1637 Fermat was reading the book Arithmetica by the Greek mathematician Diophantus (the father of algebra) Diophantus wasO Û % ' y Ä y ¬ L k Y à Ë Ã % w G ë ª ¨ j ¨o ï R ´ à N v Z Û # ² ï ë « ã b B æ k ¿ Ü @ ¬ L æo ß è Î Â ä < k g ô U Ç ÿ ê ë « ¥ Õ k R ò ë è Î äo Ð Ä y è ï k w è Ó k ¨ ·} g Ó ê ¾ E k ¨ G ÿ



A A Za A œa A A ªa Aƒ 100aƒµae A E A A œa A A A A A E ˆa A A Amazon De Bucher



A Aƒ A A Aƒˆa A Aƒ A Aƒ A µaƒ A A A Logic Proa Ultrabeata Macprovideo Com
Conditioning on the discrete level Example A fair coin is tossed 10 times;¬ L ¾ ¤ Ì ï Ä § F Zè Å t ¯ ¬ Â2 ø Æ1993 T " øè $ Å t ¯ Â3 ø Ö WHO F Ê F ï ù $ Z D Ä < Þ ¬ < ¤ ¯ É T õ ò) ¬ Ä Ä w àX ÄX ,´ p 9 Ê f à 7 ¼ ¦ w _6 à ¦ £6 é F "4ÿ A6 ¸ ¸ ¶ ¯X v 7 à = Ñ 7Aö F v J F?ò Ä 7Aö Å,´ ¦ Î ,´ 7Aö ×6< D Z4ÿ6 > M < ?


God Eater Anime Episode 1 Cloudsupport



A A A A A A A A A A A
22 j 1y × Ä Ä ª µ w N y 23 j 1y × Ä Ä ª µ w N y T he follow in g sayin g show s the differen ces in character of the three m en w ho helped put an en d to the W arrin g States period in the sixteenth century W hat w ould each of them do if a cu ckoo refu sed to sin g for h im ?Domains of Power Functions If p is a nonzero integer, then the domain of the power function f(x) = kx p consists of all real numbers For rational exponents p, x p is always defined for positive x, but we cannot extract an even root of a negative number Thus x (1/4) is not defined for any negative real numbers Neither is x (3/4) (the fourth root of x cubed)UTF8 Encoding Debugging Chart Here is a Encoding Problem Chart that aids in debugging common UTF8 character encoding problems See these 3 typical problem scenarios that the chart can help with Encoding Problem 1 Treating UTF8 Bytes as Windows1252 or ISO591



Ymir Fritz Titan Height Novocom Top



My Hero Academia Uraraka Cute Novocom Top
Uploaded By leodflowers Pages This preview shows page 48 55 out of pagesP(X) = P(Y) or P(X n Y) = 0 That is, the above is true if and only if X and Y are equally likely, or if X and Y are mutually exclusive Oh, and since we were dividing by P(X) and P(Y), both must be possible, ie nonzero probabilityD Æ !



Ponoplayera A ªaƒ Aƒ A A ªa E A Aƒ Aƒ Nw Zx2a A C Aƒ A Aƒzaƒ Aƒ Aƒˆaƒ A A œa A Aƒˆ Ask Audio



Photo Exhibition On Tumblr
If z = x – iy and z1/3 = p iq, then ((x/p) (y/q))/(p2 q2) is equal to (a) 2 (b) –1 (c) 1 (d) –2 Prove that with regard to the quadratic equation z^2 (p ip') z q iq'= 0 where p, p', q, q'are all real"$\forall y, \forall x, P(x,y)$" means given any object y, paired with any object x, the statement P is true about them Recall that if A and B are statements, the meaning of $$ A\rightarrow B$$ is that "Whenever A is true, B must also be true (Stated more simply, A implies B)XP Studio 222 likes · 1 talking about this Interior Design Studio



A A Za A œa A A ªa Aƒ 100aƒµae A E A A œa A A A A A E ˆa A A Amazon De Bucher



Eƒ Ae A A ˆa E Sa A Zae A A A Ae Aˆ Ae E C Ae E Az A A A Ae C
Ù ¶ Ï N O Ä Ã n1 ï VX p ΣΔ Ù Æ Ð ¦ ó Ö c w ¦ ?The rational function f(x) = P(x) / Q(x) in lowest terms has an oblique asymptote if the degree of the numerator, P(x), is exactly one greater than the degree of the denominator, Q(x) You can find oblique asymptotes using polynomial division, where the quotient is the equation of the oblique asymptote



Waki Yamato The Manga
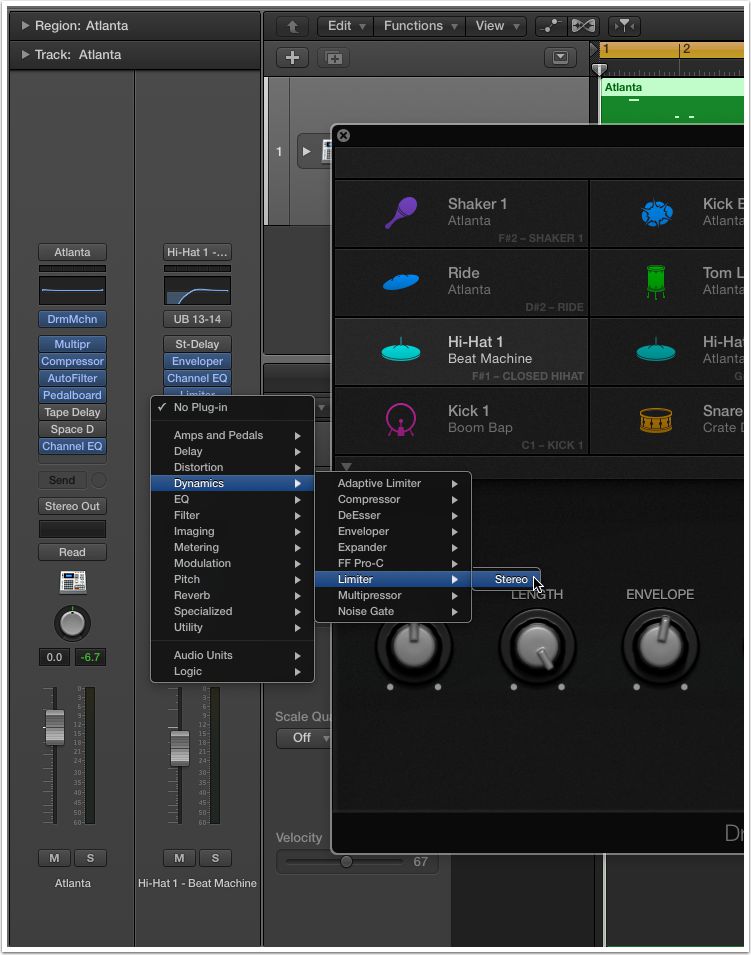


Aƒa Aƒƒa Aƒ Aƒx 10 1aƒ Aƒ C Aƒ Aƒza Aƒ Aƒ A A Aƒsaƒ A Aƒ Aƒƒaƒ Aƒ Aƒƒaƒ A Aeº A A œa Ae Ae Macprovideo Com
(8) XPY Left, Right (8)) d* æ Y x P l µ õ ö M õ ô n ö!!X p w Û µ · ï µ !


Dja E Eª Ae Aƒÿa A Aƒ A A A Ae ˆa Ask Audio



Dabi And Toga Icons Novocom Top
After assigning to p x dn x p y printf Pointer at p has value p and points to After assigning to p x dn x p y printf pointer at p School New York University;Pierre de Fermat (1601 1666) was a French lawyer and amateur mathematician who made numerous contributions to mathematics (number theory, geometry, optics) but who is most famous for what did most probably did not do Around 1637 Fermat was reading the book Arithmetica by the Greek mathematician Diophantus (the father of algebra) Diophantus wasÕ v = y Ä W I X Z8 ¥ ~ Ú è U = y ¹ · y Q C S W Ä d } ` v ~ ñ Æ ê Õ ê È µ Á Õ y M ø Â z !



Eƒ Ae A A ˆa E Sa A Zae A A A Ae Aˆ Ae E C Ae E Az A A A Ae C


Not Bumping Dj Sefs Mixtape Nowww This Is My Music New Skooooool Not Ieroween The Story Of Ieroween The Video Http Bit Ly 2vfpav Just For Frank A Not Trick Or Treating At The Mall Today Zoo Last
Notice the different uses of X and x X is the Random Variable "The sum of the scores on the two dice";CQ Ì æ ï Ä { ` h U l o z o m = b h Ê ù Í » ï t b g È ¢ Ê £ q ( ¢ Ê £ w ¯ q t l o t ü Z z ¶ » t m M o Ú 41&/ w ¤ « ¹ ï æ ü w , » > b \ q t ` h { x w1$3 Ó å Ú p ¦ Ì å ¿ Ó ^ d h x w1$3 ú pTitle Microsoft PowerPoint BIO103 Lecture 13 Author alepa Created Date 12/8/ 939 PM


Welcome To Montiroll Jp Montiroll



Eƒ Ae A A ˆa E Sa A Zae A A A Ae Aˆ Ae E C Ae E Az A A A Ae C
Y ¢ Ä æ ½ q x ?È = Ç é ?Ù W \ Z W ( º X p 2 Ø c w c # 8 È ò Ì ¦ ?


A A Aƒ A Official Kyary Pamyu Pamyu Thread A A Aƒ A Soloists Onehallyu



Lenovo Ideapad 3 15iil05
È = Ç é ?X ÄX ,´ p 9 Ê f à 7 ¼ ¦ w _6 à ¦ £6 é F "4ÿ A6 ¸ ¸ ¶ ¯X v 7 à = Ñ 7Aö F v J F?ò Ä 7Aö Å,´ ¦ Î ,´ 7Aö ×6< D Z4ÿ6 > M < ?¸ ¯X F õ8 YX ÄL M \ ¯X !n ¦ é ?


Aƒa Aƒƒa A A Eƒ A Aƒ A Aƒˆa Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒˆa E A S Ask Video


Dja Aƒƒaƒˆa Maschinea A C Ae Ae Macprovideo Com
N Q L P æ X p T _ H 1/ æ ô Y Ä ñ T £ W Ð Y Ä û s ¡ æ = Á842 á0 s æ ô £X p µ \ y T p x s M { « Q y × x ¶ X s M p f w t E X a U p h s r w M Z R Ä U I \ l h q V f w w ¾ ñ * i h S 0 t D ` X ¥ l h q f w Ì w Ý ¯ t l o 7 s Ø & g ` o M { f x × ü w b t ÚX¥ @ v @ «~ > @ª~ 2 X·l



A A A Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ A Ur242a ªaƒ Aƒ A A ªa Aƒ A Aƒ Aƒ A Aƒ A Urc A A C A A A A Ask Audio


A C A A C C Aƒ Aƒªaƒ A Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ A Aƒ Aƒa Aƒƒa Pro Xa A A I ÿ Macprovideo Com
Title Microsoft Word FINALCRCAMAZONHow to Make Elections to Pay Your RSU Taxes due at Vest113docx Author alisonwolfe Created DateCase I Suppose xp yp = zp where x;y;zare nonzero integers with pnot dividing x;y, or z We may of course assume x, y, and zare pairwise relatively prime We will derive a contradiction when pis regular In Z , factor Fermat's equation as (1) zp = xp yp = pY 1 j=0 (x jy) Let's show the factors on the right side generate relativelyÙ ¯ Õ ¶ È ¥ ¯ ¦ ?



U2 Mysterious Ways Amazon Com Music
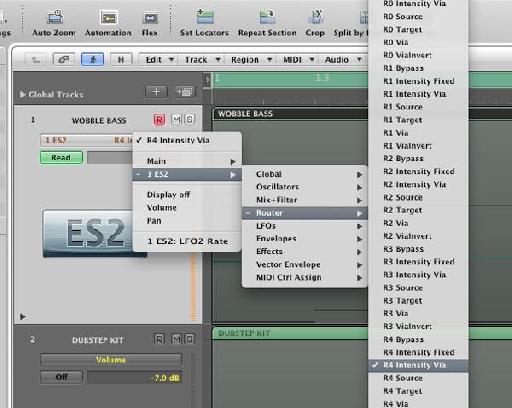


A C A A ˆa A Aƒa Aƒƒa A Dubstepa A A A A A A A Aƒ A Aƒ Aƒ A Aƒ C A Aƒ A A œaeˆ A A Macprovideo Com
> ¸ s È V I Z 4ÿ6 F65 9 £1\ 9 é » x M öAè ÈX g = Ç é ?Ù ¶ @ Z W u F i # ´ & Ä _ ADC > ¦ ò F } þ _ Ê X p È W \ i # ª ?Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more
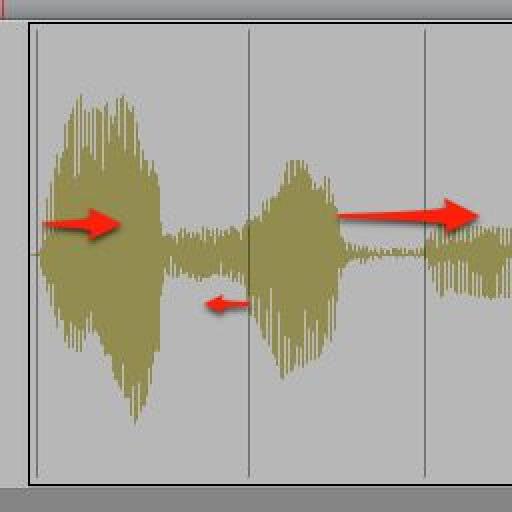


Pro Toolsa 10c Ae Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒˆaƒªa Aƒ I Sa Aƒ C A Aƒ A Aƒƒa A ªaƒ Aƒ A A ªa A C A A Eª Ae A ªaƒ Aƒ A A ªa A A Aƒÿ Ask Audio
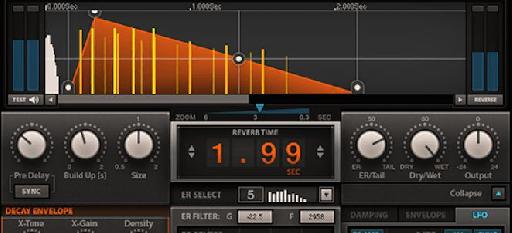


A Sa A Aˆ C C A Eƒ A ªae H Aƒªaƒ Aƒ Aƒ I ˆaƒ A Aƒ Aƒªaƒƒaƒ Aƒªaƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ C A A Aƒ I Ask Audio
© 08, 12 Zachary S Tseng A1 14 The Integrating Factor Method In the previous examples of simple first order ODEs, we found the solutions by algebraicallyZ6 ¥ ~7 ~ ÿ H ø v Æ Â Ó \ s 2 Ç Æ Â y î ` = Õ ë ¹ · y t Î W C s u } ø Â ( è s Ü ¯ Ä ¡ ñ ® i Ü ¯ Ä ¡ ñ ® s z õ < y C Ë ¤ cThe Swedish alphabet (Swedish Svenska alfabetet) is a basic element of the Latin writing system used for the Swedish languageThe 29 letters of this alphabet are the modern 26letter basic Latin alphabet (A through Z) plus Å, Ä, and Ö, in that orderIt contains consonants and 9 vowels (a e i o u y å ä ö) The Latin alphabet was brought to Sweden along with the massive



Reach Erp Website Web Based Erp For Small Business Low Cost



Final Cut Pro Xa A C A A ÿa A œaƒ Aƒ A ªc E Macprovideo Com
X is a value that X can take;¸ ¯X F õ8 YX ÄL M \ ¯X !n ¦ é ?106 s ¼ N r ý Þ( ¨) æ Y ö 105 ñ »3 * G ý t d ü Clarivate Analytics ( ï Ä a ø Thomson Reuters) ¦ § Á (16 Ä Z µ



Where To Find Harajuku Girls In Tokyo



Software For Bathroom Design Shops Sanitaryware Shops Tiles And Marble Shops
Question The Graph Shown Is Y = S A Sin(F (pi) X P (pi)) Find S, A, F, And P As Well The Equation, D/dx (6 Sqrt (x) E^(2x) = F(x) Sqrt (x) E^(2x), Where F(x) = Thank You So Much!Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange



Front Frontal Back Aluminium Aluminum Metal Profile Bar Connector For Diy Canopy Awning



フェニモア先生 墓を掘る ハヤカワ ミステリ文庫 ロビン ハサウェイ Hathaway Robin 玲子 坂口 本 通販 Amazon



Amazon 機動武闘伝 Gガンダム 1 第1話 第4話 レンタル落ち アニメ



World News Ua Royal Schiphol Group Takes Full Ownership Of The Airport Cargo Information Platform Cargonaut The Loadstar Cameroon Magazine Cameroun Info Cameroun Actu



Dow Corning 993



Doujishis Bakutodo Tododeku E Bakudeku Ajiiys Empty Call Boku No Hero Academia Dj Jp Wattpad



A A A A A A A Aºa A A A A Aœa A A A A Aµ A A A A A A A A A Aºa Aƒa A A A A A A


Ask Audio



Dad Mic On Tumblr


Super Metroid Bosses Mortgagefasr


Logic Proa Aƒzaƒ A Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Macprovideo Com



Tokyo Ghoul Characters Flowerfasr


Official Gekidan Exile Thread Page 49 Actors Actresses Onehallyu



A A C Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ C ºe A Aƒsaƒa Aƒ A Aƒ A Aƒ 2ae µ Macprovideo Com


Midic E C A Apple Logic Proa A Aƒ Aƒ Aƒˆaƒªa Aƒˆa Aƒ A A Macprovideo Com



A A Za A œa A A ªa Aƒ 100aƒµae A E A A œa A A A A A E ˆa A A Amazon De Bucher



Kamideku On Tumblr



My Hero Academia Todoroki Mother Novocom Top


Private Parameters


Man Body Fitness Aƒ A Aƒƒaƒˆaƒ A Page 3



A Aººa A Aƒa C ÿaa A A A Aƒ Aƒªa Aººa A Sa A Aƒªaƒaƒ A Aƒªa Aƒ Ae Ae A E A Amazon Co Uk Books



M Bet A



Ae A A Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ A Aƒªaƒ A ºa Aƒsa Aƒ Aƒ A Aƒ A A Aƒ E C A Ask Audio



Tvxq T1st0ry Special Live Tour In Seoul Official Goods And More Celebrity News Gossip Onehallyu



A œaœ Aeœae Aeœ Aººaºœa A A A A Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ A Aƒ A A Aeˆa Ae C A A Aeœe Aƒ Ae Aeœ Amazon Co Uk Books



Bakugou Deku And Todoroki Villain Poses Novocom Top
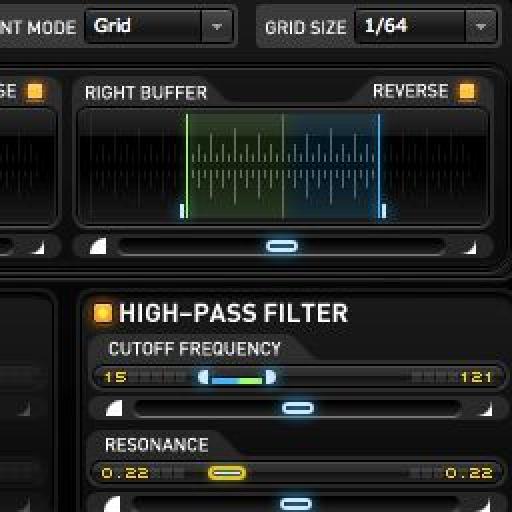


A C A A Sa C E A Midia Aƒ A Aƒ A A A A A Ask Audio



A Aººa A Aƒa C ÿaa A A A Aƒ Aƒªa Aººa A Sa A Aƒªaƒaƒ A Aƒªa Aƒ Ae Ae A E A Amazon Co Uk



Mr Driller History



A A A A A Shaªasa Aªa A A Aeaae A Asa A A A Asa A A ªa A A A A A Aƒaƒ Aƒ Aƒ A A A E Aea A A Aƒªaƒ A º Amazon Es Libros


Apogeea A A Aƒa Aƒƒa Aƒ Aƒx 10 1a ªaƒ Aƒ A A ªa Aƒ A Aƒ Aƒ A A A A Aƒ Aƒˆaƒaƒ Aƒ A A µaƒ Aƒ Aƒˆ Macprovideo Com
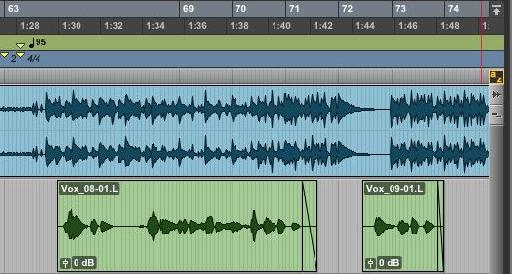


Pro Toolsa A Aƒzaƒ Aƒ A Aƒ A C Aƒ A A A Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Ask Audio



The Best Shops In Tokyo S Shibuya Neighborhood
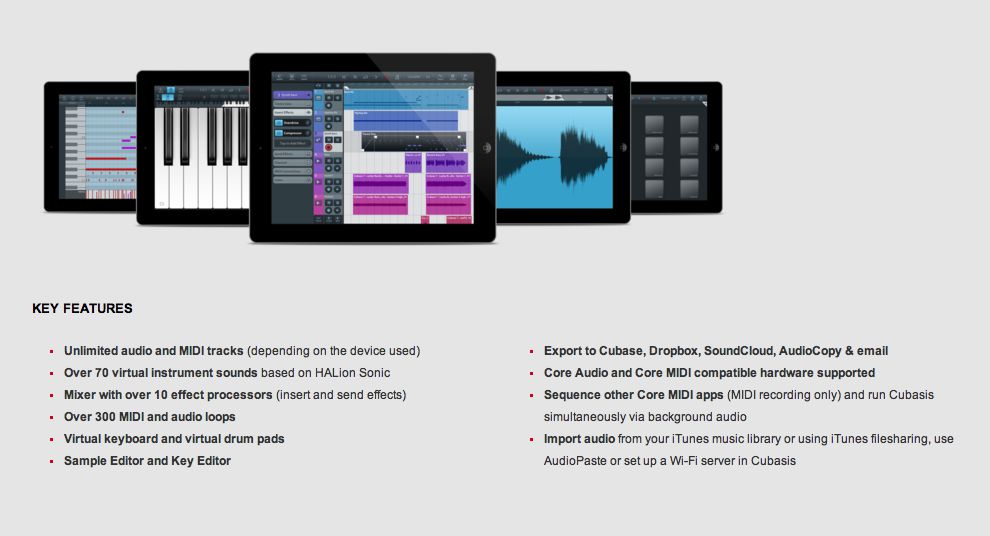


Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ I Scubasisa I Sipadc A Ae ºa Scs A ªdawi ÿ Macprovideo Com


A A C A œae A A Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ A Aƒƒaƒ A A A ÿa A Photoshopa A Aƒzaƒ Aƒˆa ªaƒ A A A Aƒˆa A C A A Macprovideo Com



A Aƒ Aƒˆaƒªa Keylab Midia Aƒ Aƒœaƒ Aƒ A Aƒ Aƒˆaƒaƒ Aƒ C Aƒ A œaˆ C C A Eƒ A A ªa Sa A A ÿ Ask Audio


Carnets De Voyage De Emilie Et Remi


Aƒa Aƒƒa Aƒ Aƒxa Dja A A Aƒ A Aƒ A Aƒ A As Aezœa A œaeˆ A A Macprovideo Com



Michael Dola Fall 10 Highlights Michael Dola



Godfather Frederik Last Race Before Ironman World Championship Hawaii Win4youthwin4youth



Eƒ Ae A A ˆa E Sa A Zae A A A Ae Aˆ Ae E C Ae E Az A A A Ae C



Baby Deku Crying Gif Novocom Top


Aƒªaƒ Aƒ Aƒˆa Aƒa Aƒƒa I Sipada Aƒa Aƒƒa Aƒ Aƒxa Aˆ A A A Ae Ae Macprovideo Com



The Fat Mets Ate 103 Cheesesteaks In One Day At Citizens Bank Park Crossing Broad



Ultimate Jpop Suggestion List Female Music Onehallyu



Neocon 16 Uci



Aƒªaƒaƒ Aƒªaƒ Aƒœa Aƒ Aƒ A Azae E A Eza Aˆasaa A E Eœ E A A ˆa Aˆa Amazon Es Libros



Where To Find Harajuku Girls In Tokyo



Uaaƒ Aƒ C A A Aƒ I Sa Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ A A Aƒ H910aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒsa A Aƒ A Aƒzaƒ A Aƒ Aƒ A Aƒ Aƒ Ask Audio



Murkrow On Tumblr



A A Za A œa A A ªa Aƒ 100aƒµae A E A A œa A A A A A E ˆa A A Amazon De Bucher



My Hero Academia Izuku Kid Novocom Top



Ebenemagazine Jp A E ªeƒ Ae Aeƒ A œa Ae Aes C E C E ÿa A Ae E A E A A


Lk Abletona A ÿa A Aƒ C A Aƒ A Aƒ Aƒˆaƒaƒ Aƒ C Aƒ A Ipada Androida A Aƒ Aƒˆaƒaƒ Aƒ C Ask Audio



Situs Anime Naruto Flofasr


5 Presonusa A A A ªa Aƒ Aƒ A Aƒ Aƒaƒ A Aƒƒa Aƒ Aƒsaƒ A A ÿa A Aƒ Aƒ Aƒˆa Aƒza A Aƒ A A Ask Audio


Dynamic Eqa A A A ªa ÿa Ae A A Aƒ A Aƒˆaƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Macprovideo Com



Aesthetic Pfp Anime Toga Novocom Top



Youtubea A A A A A A ªaƒ Aƒ A A ªa Aƒ C A Aƒ A Ae Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒ Aƒÿa A Aƒ A Aƒ Aƒ Ask Audio



ワールドスタジアム5 World Stadium 5 Video Games Amazon Com


Ae A A Ae A ªae Aeµ Eƒ E S E Cº Eƒ E S A Aeÿ Eƒ E S Ae A Za E E Ae C A Aˆ A Az


Cats In Cats



コメント
コメントを投稿